Proposing Solutions for Transportation Robots

All industries are currently facing labor shortages due to declining birthrates and an aging population, while social distancing is becoming an issue to prevent the spread of COVID-19. Against this backdrop, companies are accelerating their efforts to automate and reduce the number of workers in the comparatively simple "task of transporting goods." Introducing transportation robots (AGV/AMR/GTP*) is being promoted as a solution to this problem.
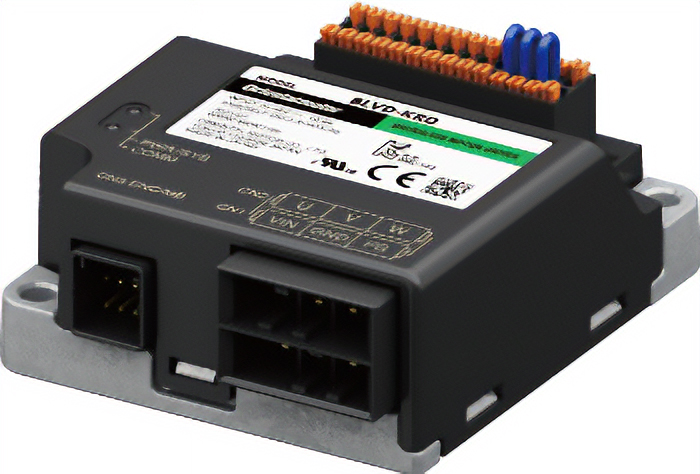
The BLV Series R type and BLH Series brushless motors can be driven by battery, so they can be used on the shafts of transportation robots or mounted on transportation equipment.
This contributes to being able to handle the wide variety of travel patterns and loads required in a variety of fields.
- *AGV: Automatic Guided Vehicle AMR: Autonomous Mobile Robot GTP: Goods To Person
Low Clearance and Slim Design: The Body Can be Used in Any Cargo Shape or Location
Automatic Transportation by Moving under Basket Dollies or Shelves: Low Clearance Design
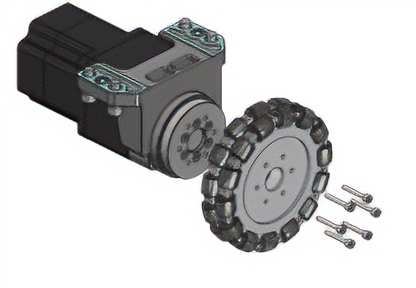
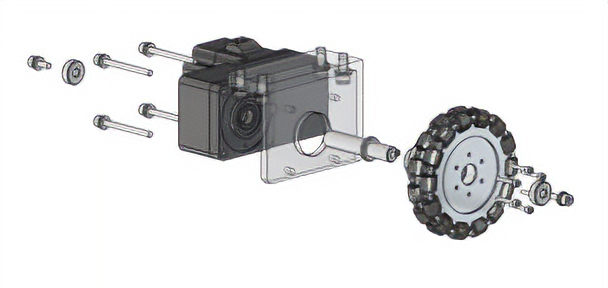
Low clearance transportation robots are effective in transportation operation automation because they can move under product/part shelves and basket dollies to lift (or secure) them. The motor can be mounted on either the top or the side, allowing for greater design flexibility and contributing to low clearance designs.
-
Top Mounting Flange Drive Adapter

-
Side Mounting Hollow Shaft Flat Gearhead

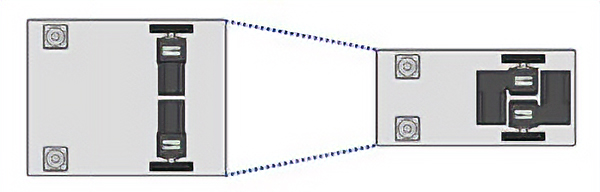
Passing on Narrow Aisles: Slim Design
An arrangement of intersecting hollow shaft flat gearheads reduces the distance between wheels, allowing for slimmer designs and reduced vehicle width. This allows transportation robots to pass each other even in narrow aisles, reducing transportation robot wait times and contributing to improved operating ratios.
Even lower and slimmer
Compact, flat drivers
The compact size expands the degree of layout freedom for installation locations of batteries, control devices, and more.
-
BLV Series R type
60 W, 100 W,
200 W, 400 W -
BLH Series
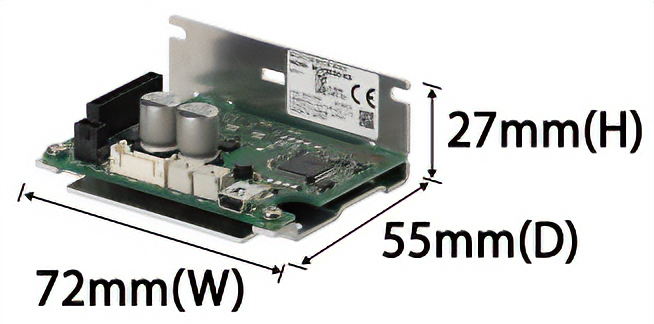
15 W, 30 W, 50 W -
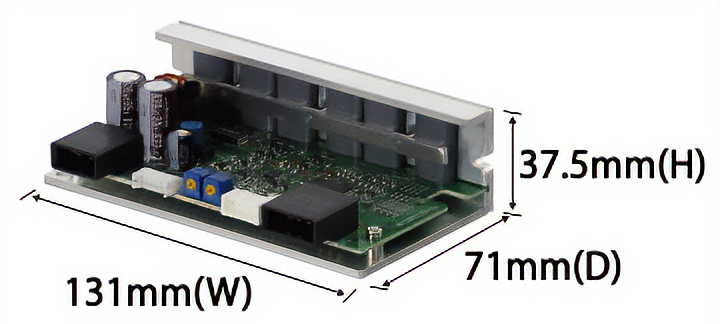
100 W -

Electric brakes *
Electric brakes maintain the stop position when stopped, so no mechanical brakes (electromagnetic brakes) are required. Because the motor's overall length can be shortened, designs with reduced vehicle width are possible.
- *Applicable only when power is supplied.
High Load Performance: Applicable for Large Loads and Robot and Conveyor Installations
The permissible radial load affects the load-performance capacity of transportation robots. When the flange drive adapter is assembled, it has a high strength of 1500 N (153 kgf) and the hollow shaft flat gearhead has a maximum strength of 2040 N (208 kgf). This supports the requirements of larger loads and mounting on robots and conveyors.
| Gear Ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 50 | 100 | 200 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| When the Flange Drive Adapter is Assembled | 100 W*1 | 1500 | |||||||
| Hollow Shaft Flat Gearhead | 200 W, 400 W*2 |
1230 | 1680 | 2040 | |||||
| 100 W | 900 | 1300 | 1500 | ||||||
| 50 W, 60 W |
800 | 1200 | |||||||
| 30 W | 450 | 500 | |||||||
- *1
- Motor shaft speed of ~300 r/min
- *2
- Motor shaft speed of 100~3000 r/min

Stop Position Setting and Fine Adjustments: Link Smoothly With Prior and Successive Processes
Setting the Remaining Travel Distance From a Specified Position: Position Control
Setting the travel amount is similar to stepper motors and servo motors. In addition to transportation of a predetermined distance on the guide, partial positioning operations are also possible, such as setting the distance from the sensor input position to the target stop position during autonomous driving.
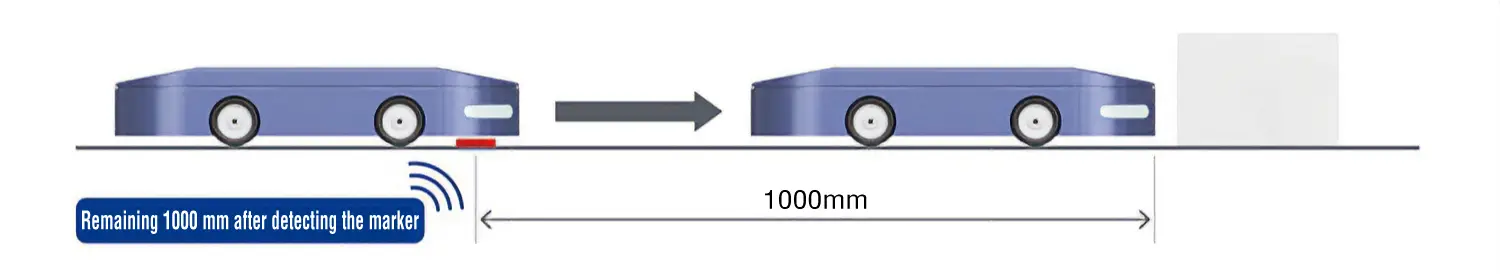
Fine Adjustments to Stop Position: Speed Control
The motor shaft rotation speed can be set from 1 r/min. If this is substituted with transfer speed, it equals approximately 0.3 m/min for a wheel with a diameter of 100 mm. This allows for very low speeds, small overrun, and fine adjustments to stop positions.
The maximum rotation speed is 4000 r/min, which contributes to shortened takt times by increasing the transfer speed.
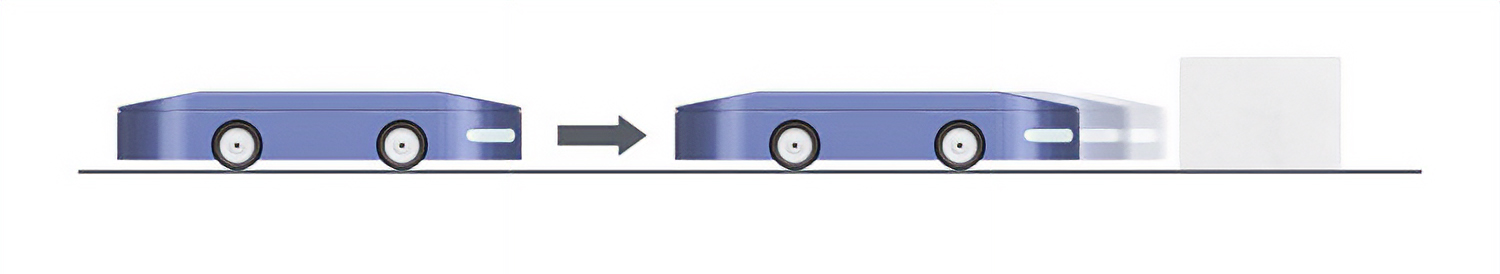
Holds vehicles in place and stabilizes transfer operations
Mechanical brakes (electromagnetic brakes) or electrical brakes can be installed to hold the vehicle in place when stopped. It stabilizes operations by preventing vehicles from shifting, even while transferring or tilting.
Straight Movement, Avoiding, and Stopping: Flexible Adjustment of the Transportation Robot's Path
Transportation robots require travel performance that can respond to a variety of changes like floor conditions and avoiding sudden obstacles. The feedback signal from the motor and the corresponding commands to each shaft can be executed smoothly, enabling flexible adjustments to moving straight, avoiding, and stopping.
High resolution sensor equipped
The sensor’s maximum control resolution is 36000 P/R. It provides a detailed understanding of driving conditions and present position.
Direct data operation
Responses to sensor information allow for flexible operations like emergency braking and speed resets during operation.
ID share mode and broadcast mode
Commands can be sent to multiple vehicle shafts simultaneously, allowing for sudden turning movements and preventing zig-zagging when initiating movement.
Useful functions during adjustment
Various settings are available in the network
- BLV Series R type
-
 ,
,
- BLH Series
-
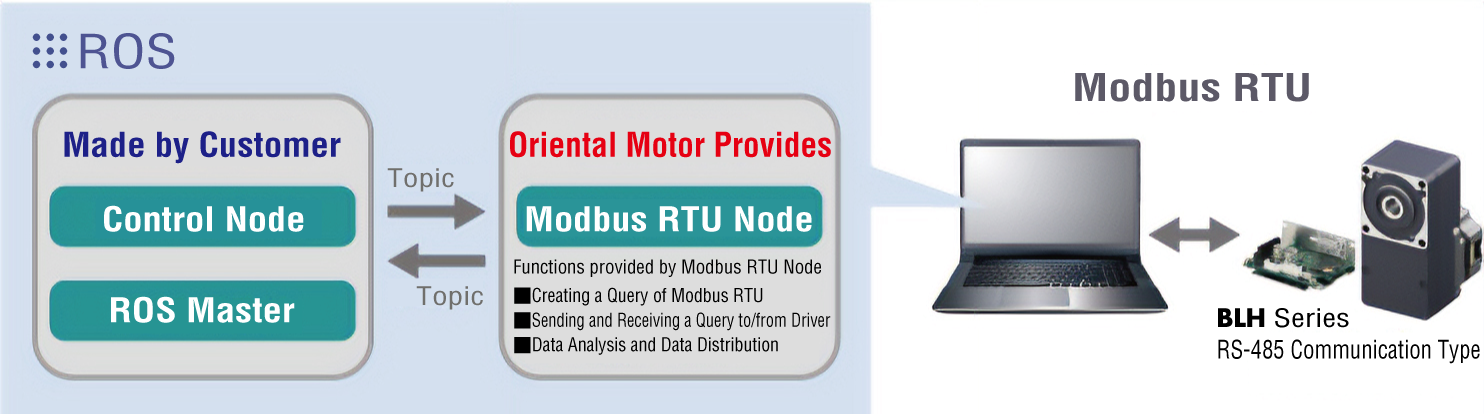
The BLV Series R type and BLH Series can be controlled by software created in "ROS."
- The BLV Series R type cannot use ID share mode when it is controlled by software created in "ROS."
Gain adjustment according to the load
Gain (responsiveness) can be adjusted according to the load. This contributes to stable driving.
Status monitoring
The monitoring function in the support software allows you to monitor status. The BLV Series R type is also equipped with a trace monitor, allowing for continuous measurement for maximum 1 full day. This will contribute to clarifying the cause of any problems that may arise.
- *CiA® and CANopen® are registered trademarks of CAN in Automation e.V.
- *Modbus (RTU) is a registered trademark of Schneider Automation Inc.
Compatible Products
-
-
-
The BLH Series are also sold as stand-alone motors.
-
| Features Introduced | Output | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 W | 30 W | 50 W | 60 W | 100 W | 200 W | 400 W | |||
| Low clearance and slim design High load performance |
output shaft | Hollow Shaft Flat Gearhead | ● ● | ● ● | ● | ● ● | ● | ● | |
| Flange Drive Adapter | ● ● | ||||||||
| Compact, flat drivers | ● ● | ● ● | ● ● | ● | ● ● | ● | ● | ||
| Electromagnetic Brake | ● ● | ● ● | ● ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Electric Brake | Load Hold Function | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| S-ON | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Stop Position Setting and Fine Adjustments |
Position Control | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Speed Control | 1~4000 r/min | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| 80~3000 r/min | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 100~3000 r/min | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Moving Straight Avoiding Stopping |
High Resolution Sensor | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Direct data operation | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Data Transmission | ID Share Mode | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Broadcast Mode | ●※ | ●※ | ●※ | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Compatible Network | Modbus (RTU) | ●※ | ●※ | ●※ | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| CANopen | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Gain Adjustment | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Support Software | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
- *RS-485 communication type only